Daycare Financial Model

- ✔ 5-Year Financial Projections
- ✔ 100% Editable
- ✔ Investor-Approved Valuation Models
- ✔ MAC/PC Compatible, Fully Unlocked
- ✔ No Accounting Or Financial Knowledge
Daycare Financial Model
Bundle Includes:
ALL IN ONE MEGA PACK - CONSIST OF:
daycare Financial Model/Business Plan Excel Template
Pitch Deck Template For PowerPoint, Keynote & Google Slides
Business Plan Guide and Business Plan Template in MS Word Format
Financial Dashboard in Excel To Track Your Business Performance
BUSINESS PLAN FOR DAYCARE INFO
Highlights
A comprehensive daycare budgeting strategy is essential for entrepreneurs launching a childcare center, as it provides a detailed financial plan that includes startup costs, operational expenses, and revenue projections. This template incorporates key financial statements and metrics, enabling effective expenses analysis and cash flow management for daycare operations. By utilizing a structured daycare pricing structure and conducting a daycare break-even analysis, owners can assess profit margins and determine sustainable funding options. The investment analysis for daycare will facilitate informed decision-making regarding funding forecasts and help secure financial backing from banks or investors. Overall, this tool is designed to support financial sustainability in the childcare sector while ensuring a robust understanding of daycare revenue streams and operational budgeting.
Designed to address common pain points for daycare center owners, this financial model offers an intuitive yet comprehensive approach to daycare budgeting strategy, enabling users to efficiently analyze operational costs for daycare alongside revenue projections. The template simplifies expenses analysis childcare and provides clarity on daycare pricing structure, ensuring accurate tuition fee calculations that align with market standards. Users can leverage the financial forecasting childcare features to assess profit margins in daycare, facilitating informed decisions related to startup costs and break-even analysis. With robust cash flow management tools and insights into daycare funding options and revenue streams, this model ensures long-term financial sustainability childcare while offering detailed financial reporting for childcare that showcases the viability of their business plan to potential investors.
Description
The daycare financial projection template in Excel is an essential tool designed to assist users in developing a comprehensive childcare financial plan that forecasts operational costs, revenue projections, and profit margins for both startup and existing daycare centers over a 60-month period. This user-friendly model offers detailed financial reporting for childcare, including a profit and loss forecast, a pro forma balance sheet, and a projected cash flow statement tailored to the specific needs of daycare services. It incorporates expenses analysis childcare, daycare pricing structure, and tuition fee calculations, allowing for effective cash flow management daycare and an in-depth daycare break-even analysis. Additionally, the template includes valuable features such as cost-benefit analysis daycare, investment analysis for daycare, and various daycare funding options, ensuring users can strategize for financial sustainability and make informed decisions to optimize daycare revenue streams.
BUSINESS PLAN FOR DAYCARE CENTER REPORTS
All in One Place
A robust daycare budgeting strategy is essential for financial sustainability. A comprehensive five-year projection plan incorporates operational costs, revenue projections, and expenses analysis childcare. By consolidating financial statements—including cash flow, pro forma balance, and income forecasts—daycare centers can ensure effective cash flow management. This exhaustive financial model allows for informed tuition fee calculations and identifies daycare funding options. Ultimately, a well-structured daycare financial plan supports strategic decision-making, enhances profit margins, and aids in break-even analysis, leading to a thriving childcare business.

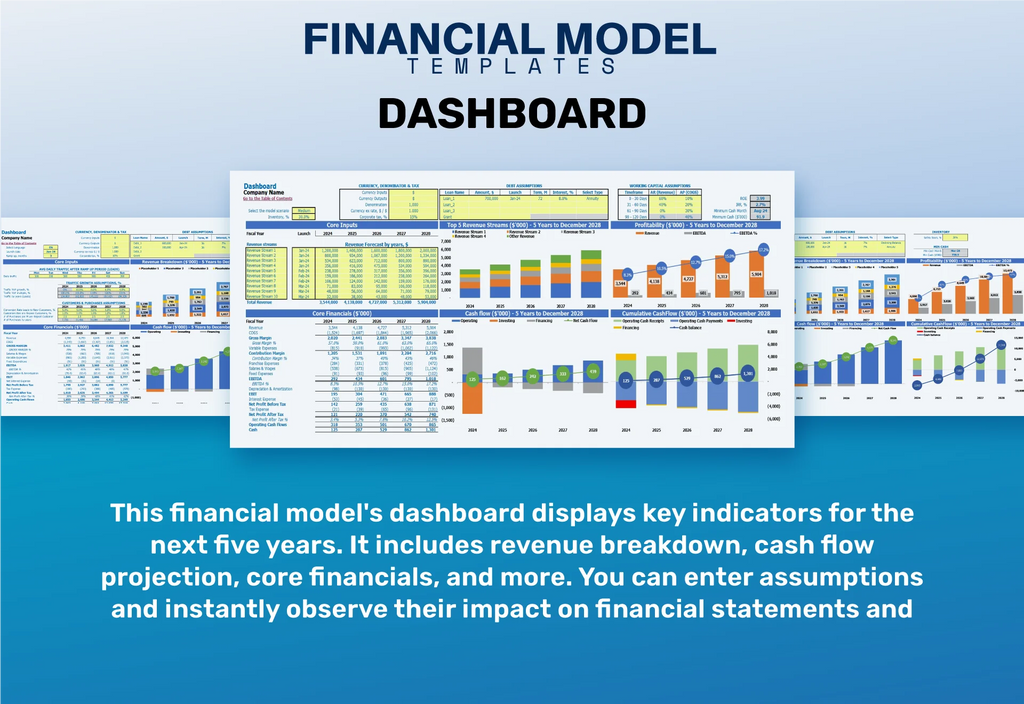
Dashboard
Elevate your daycare financial planning with our innovative tool. Input your data to generate visually appealing financial forecasts, ensuring your daycare budgeting strategy is robust and compelling. Instantly access professional charts for revenue projections, operational costs, and expense analysis, ready for your presentation deck. Whether you're assessing startup costs or analyzing profit margins, our tool simplifies the process of evaluating tuition fee calculations and daycare funding options. Achieve financial sustainability with accurate financial reporting and insights into cash flow management. Make informed decisions for your childcare center today!
Business Financial Statements
Our comprehensive financial projections spreadsheet offers an integrated approach to daycare budgeting strategy, allowing users to easily create a projected balance sheet, forecasted income statement, and cash flow pro forma. With the ability to input historical or forecasted data, this tool facilitates detailed expenses analysis childcare and revenue projections for daycare. Stakeholders can explore the implications of various operational decisions, such as tuition fee calculations and daycare pricing structure, enhancing financial sustainability childcare. This streamlined tool supports effective cash flow management daycare and strengthens overall profit margins in daycare centers, ensuring informed decision-making for long-term success.

Sources And Uses Statement
Effective daycare budgeting strategies hinge on a thorough understanding of sources and uses of funds. By meticulously tracking income streams and operational costs for daycare, you can optimize your childcare financial plan. This clarity aids in expenses analysis childcare, ensuring sound tuition fee calculations and revenue projections for daycare. Moreover, it facilitates robust financial reporting for childcare, enhancing cash flow management daycare. Ultimately, precise financial forecasting childcare supports the long-term financial sustainability of your center, allowing for informed decisions regarding daycare funding options and investment analysis for daycare.

Break Even Point In Sales Dollars
Break-even analysis is essential for determining when your daycare will cover operational costs and start generating profit. To conduct this analysis, differentiate between fixed and variable expenses. Fixed costs, such as rent and administrative salaries, remain constant regardless of enrollment, while variable costs fluctuate with the number of children served, including supplies and staffing. This understanding is pivotal for effective daycare budgeting strategies, ensuring financial sustainability and guiding revenue projections. By mastering break-even calculations, you can enhance your daycare's financial forecasting and optimize profit margins, ultimately securing a thriving childcare financial plan.

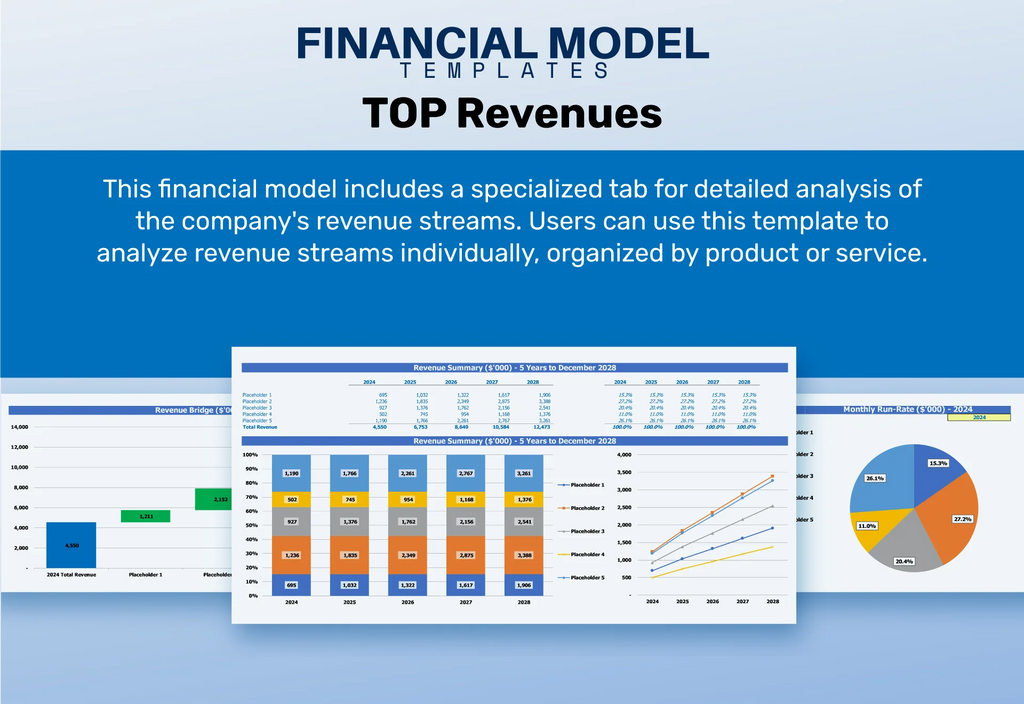
Top Revenue
Utilize our Excel pro forma template for an engaging overview of daycare revenue streams. The Top Revenue tab provides a detailed analysis of financial projections, allowing you to explore the complexities of your daycare pricing structure. With insights into operational costs and revenue depth, you can develop an effective childcare financial plan. This comprehensive tool aids in expenses analysis and cash flow management, equipping daycare owners with the necessary information for informed decision-making and financial sustainability. Enhance your daycare budgeting strategy and optimize profit margins with our intuitive financial forecasting capabilities.
Business Top Expenses Spreadsheet
In the "Top Expenses" section of our daycare budgeting strategy, company expenses are categorized into four distinct groups. Our business revenue model template includes an "Other" category, allowing you to input specific data tailored to your childcare financial plan. To enhance financial forecasting, you can create pro forma projections that extend up to five years, facilitating a thorough expenses analysis for childcare. This ensures effective cash flow management and supports your daycare's financial sustainability while tracking performance and optimizing profit margins in daycare operations. Streamline your operational budget with comprehensive financial reporting tools.

SMALL DAYCARE BUSINESS PLAN EXPENSES
Costs
Our comprehensive five-year financial forecasting plan is essential for estimating operational costs for your daycare center. It enables effective expenses analysis and revenue projections, helping you identify potential challenges early. This organized model reveals critical insights into cash flow management and daycare pricing structures, allowing you to concentrate resources where they matter most. Investors and creditors alike highly value this strategic tool, as it supports financial sustainability and informs crucial decisions like tuition fee calculations and daycare break-even analysis. Equip your childcare business with the insights needed for informed growth and profitability.

CAPEX Spending
Capital expenditure (CAPEX) is vital for a robust childcare financial plan, particularly for a startup daycare center. Financial analysts project CAPEX to assess investments in fixed assets, ensuring effective management of depreciation and acquisitions related to property, plant, and equipment (PPE). This budgeting strategy is crucial for optimizing operational costs for daycare, facilitating accurate expenses analysis childcare, and enhancing profit margins in daycare. By incorporating CAPEX into the operational budget, daycare centers can strategically plan for future growth and maintain financial sustainability, ensuring a thriving environment for both staff and children.

Loan Financing Calculator
Our daycare financial plan features a comprehensive loan amortization schedule, designed to streamline your loan repayment strategy. This template includes pre-built formulas to clearly outline monthly, quarterly, and yearly installments, detailing principal and interest amounts. By integrating this tool into your daycare budgeting strategy, you can enhance cash flow management and achieve financial sustainability. With accurate financial forecasting and expense analysis, your daycare can optimize its operational budget, ensuring healthy profit margins and effective revenue projections while planning for future growth.

BUSINESS PLAN TEMPLATE FOR DAYCARE CENTER METRICS
Financial KPIs
In your daycare budgeting strategy, key performance indicators (KPIs) are essential for both owners and investors. These metrics enable you to assess your childcare financial plan and analyze operational costs for daycare effectively. By tracking these indicators, you can evaluate your daycare pricing structure and revenue projections, ensuring financial sustainability. This focused approach helps you and your co-founders remain aligned with your established goals while enhancing cash flow management and supporting informed decisions around expenses analysis childcare and potential funding options. Utilize financial forecasting childcare to boost profitability and optimize your daycare’s performance.

Cash Flow Forecast Excel
A cash flow statement template is crucial for managing daycare operational budgets, focusing solely on cash inflows and outflows. Unlike a pro forma profit and loss statement that incorporates non-cash items, this template ensures a clear view of liquidity. Incorporating a built-in cash flow projection feature, it offers monthly forecasts for up to 5 years, aiding in effective daycare budgeting strategy development. By understanding these financial dynamics, childcare providers can make informed decisions that enhance financial sustainability and optimize profit margins, ultimately ensuring a robust financial plan for their daycare center.

KPI Benchmarks
Our comprehensive 5-year cash flow projection template features a tailored benchmarking study specifically for daycare providers. This tool offers critical insights into operational costs for daycare, enabling stakeholders to assess performance against industry standards. With a focus on daycare financial sustainability, you'll identify key areas for optimizing your daycare budgeting strategy and revenue projections. Use this template to enhance your financial forecasting childcare efforts and streamline your daycare pricing structure, ensuring you achieve the best profit margins in daycare. Elevate your childcare financial plan today and pave the way for long-term success.

P&L Statement Excel
Utilizing a profit and loss projection template is essential for understanding your daycare's future financial performance. By analyzing historical income and operational costs, you can create a robust childcare financial plan that identifies key revenue streams and potential shortfalls. This strategic approach allows you to optimize your daycare pricing structure and enhance profit margins while ensuring financial sustainability. Through diligent financial forecasting and expense analysis, you can confidently navigate your daycare's funding options and cash flow management, ultimately achieving a well-rounded operational budget that supports long-term success.

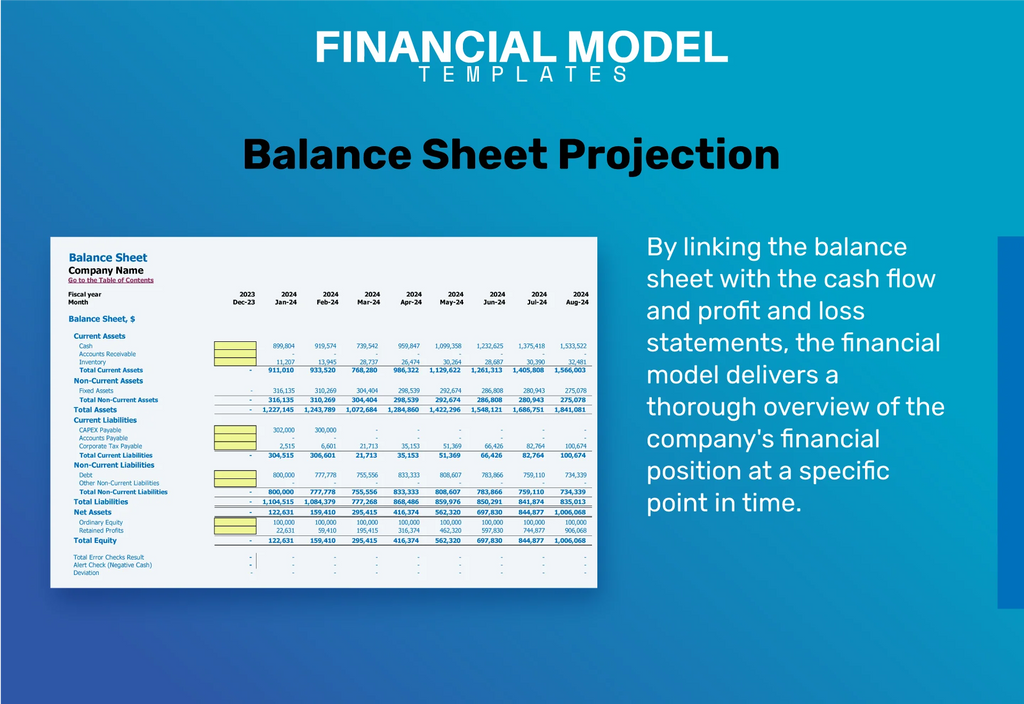
Pro Forma Balance Sheet Template Excel
A pro forma balance sheet is essential for developing a robust childcare financial plan. By outlining assets, liabilities, and capital, it aids in daycare budgeting strategy and revenue projections. Incorporate historical data over at least three years to ensure accurate assumptions for financial forecasting. Each assumption ties back to your profit margins in daycare, linking operational costs and revenue streams. This integration enhances cash flow management and enables effective daycare pricing structure adjustments. Ultimately, a comprehensive balance sheet supports your daycare's financial sustainability and helps identify funding options for future growth.
BUSINESS PLAN TEMPLATE FOR DAYCARE CENTER VALUATION
Startup Valuation Model
Every business carries inherent risks, which is why we provide a startup valuation calculator sheet. This tool enables quick access to key metrics such as NPV, IRR, and ROIC. Our comprehensive financial model template for daycare centers includes essential components for assessing financial sustainability, such as operational costs, revenue projections, and cash flow management. By leveraging aggregated customer data, you can accurately forecast future cash flows, ensuring informed daycare budgeting strategies and enhancing your overall financial reporting. This insight is crucial for understanding your daycare’s profitability and guiding effective investment analysis.

Cap Table
A well-structured cap table provides vital insights into a daycare's financial health, detailing ownership distribution, share percentages among investors, and total expenditures. This foundational tool encompasses equity shares, preferred shares, and options, illustrating the daycare's financial landscape. By analyzing these elements, stakeholders can assess the operational costs for the daycare, evaluate revenue projections, and enhance cash flow management. Ultimately, a comprehensive cap table supports effective financial reporting and fosters sustainable budgeting strategies, enabling informed decisions to drive profitability and long-term growth in the childcare sector.

KEY FEATURES
A comprehensive daycare budgeting strategy enhances financial sustainability by providing clear insights into operational costs and revenue projections.
The financial model streamlines daycare budgeting strategy by consolidating all essential reports and calculations into a user-friendly Excel dashboard.
A robust daycare budgeting strategy enhances decision-making by providing clear insights into operational costs and revenue projections.
Utilize a daycare budgeting strategy to enhance operational decisions and confidently forecast the impact on cash flow and profitability.
Implementing a daycare budgeting strategy enhances financial sustainability, ensuring profitable revenue streams and effective cash flow management.
The financial planning model simplifies daycare budgeting strategies, ensuring sustainable operations without complex formulas or costly consultants.
Implementing a daycare budgeting strategy enhances financial sustainability and maximizes profit margins through effective expense analysis and revenue projections.
A cash flow forecast empowers daycare operators to strategically manage expenses and optimize revenue projections for financial sustainability.
Implementing a robust daycare budgeting strategy enhances financial sustainability and enables informed decision-making for future growth opportunities.
Utilizing a detailed cash flow forecasting model empowers daycare centers to strategically plan for growth and manage operational expenses effectively.
ADVANTAGES
Implementing a daycare financial model ensures effective cash flow management, maximizing profit margins and enhancing overall financial sustainability.
A robust daycare budgeting strategy enhances financial sustainability, attracting funding and ensuring operational costs are effectively managed.
A solid daycare budgeting strategy enhances financial sustainability and maximizes profit margins through accurate expense analysis and revenue projections.
Utilize the startup financial model template to ensure robust revenue projections and enhance financial sustainability for your daycare center.
Implementing a daycare financial plan ensures stability through precise budgeting strategies and accurate revenue projections, enhancing long-term sustainability.




